
A sales bill of materials (SBOM) defines the details of the product prior to assembly in the sales stage. It is common to have more than one EBOM for a product as the design is revised. Engineers using computer-aided design or electronic design automation tools typically create the design. The engineering BOM shows the component structure from a functional perspective and consists of a mechanical or technical drawing of a product. An engineering bill of materials ( EBOM) defines assemblies and parts designed by the engineering department. The information in the manufacturing BOM is shared with all the integrated business systems involved in ordering and building the product including enterprise resource planning ( ERP), material requirements planning ( MRP) and, in some cases, a manufacturing execution system. An MBOM also includes information about the parts that require processing prior to assembly and explains how various components in a product relate to one another. A manufacturing bill of materials (MBOM) includes a comprehensive list of all the items and subassemblies required to make a manufactured, shippable finished product. The three main types of BOMs are the following: As a result, it is used in departments other than manufacturing, such as engineering, design, sales, material management and plant management. The BOM combines all the information that goes into building a final product. The information it provides includes the basic data for business processes, such as manufacturing resource planning, product costing, material provision for production and plant maintenance. A single-level bill of materials (BOM) goes through one level of assemblies to create a finished product.Ī BOM is the foundation of production planning systems. If a new product fails, a single-level BOM makes it difficult to determine which part needs to be replaced or repaired.
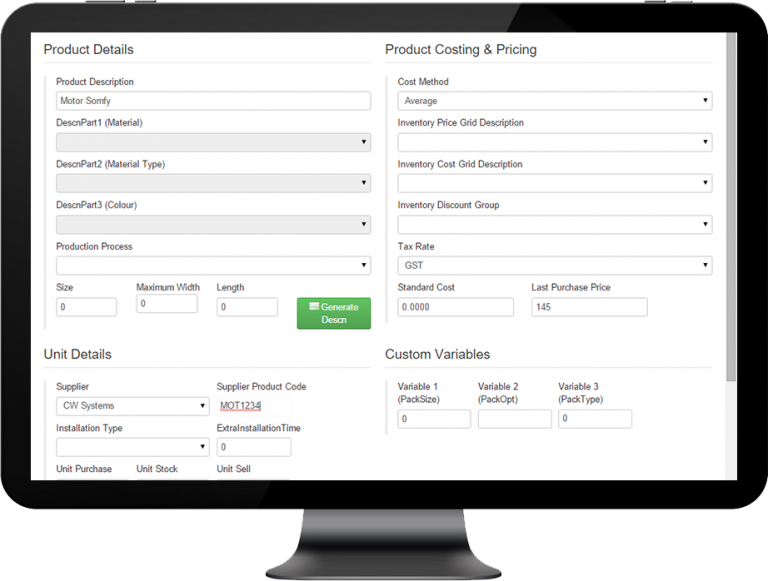

However, this type of BOM is unsuitable for complex products because it does not specify the relationship between parent and child parts and between assemblies and subassemblies. This is a simple list with each assembly or subassembly needed for a product shown once, with the corresponding quantity required for each product. It includes product codes, part descriptions, quantities, costs and additional specifications.Īmong the most common methods of representing a BOM are single-level BOMs and multilevel ones. BOM structureĪ BOM typically has a hierarchical structure with the finished end product at the top. The upfront blueprint that a BOM provides helps avoid wasteful production errors.
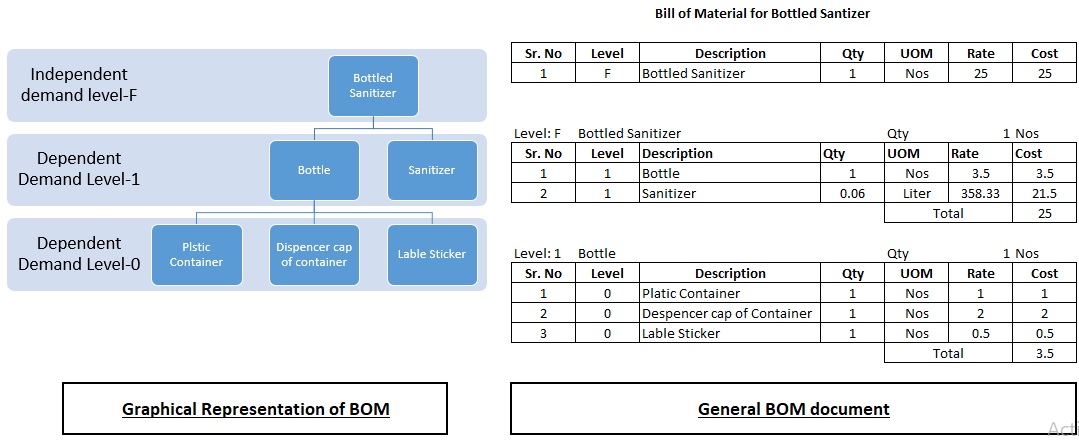
One goal of lean manufacturing is to minimize waste.
#Finale inventory bom software
find vulnerabilities in software components andīOMs help ensure third-party contract manufacturers are using efficient and accurate when production methods.īOMs are also useful for companies that run lean production and continuous improvement-based processes.identify the cause of a product failure.stay alert to materials shortages, expediting charges and planned and unplanned downtime.It lays out a detailed plan that can be easily followed.Ī well-defined BOM helps companies with the following aspects of the production process: What are the advantages of using a BOM?Ī BOM makes the manufacturing process accurate and efficient. BOMs can be created using physical products or a software-as-a-service bill of materials product. The list would include the seats, frames, brakes, handlebars, wheels, tires, chains, pedals and cranksets, as well as the quantities of each component and their cost. A BOM is sometimes referred to as a product structure, assembly component list or production recipe (in process manufacturing industries).įor example, if a bicycle manufacturer wants to build 1,000 bicycles, the bill of materials will consist of all the individual parts needed to build the bicycle.

In a nutshell, it is the complete list of all the items that are required to build a product.īOMs also include the instructions for procuring and using the materials. A bill of materials (BOM) is a comprehensive inventory of the raw materials, assemblies, subassemblies, parts and components, as well as the quantities of each needed to manufacture a product.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
